Today, Lithium-Ion and Lithium Polymer batteries are widely used in mobile electronic devices. Charging the battery effectively to extend its service life and improve its performance is of great importance in the design of electronic devices. Because, the correct charging method extends the service life of the battery, improves its performance and ensures its safety.

What is a Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Battery?
Lithium-Ion batteries, is a type of rechargeable battery technology used as a power supply in today’s mobile electronic devices and many electric vehicles. Lithium is the lightest metal available and offers a high electrochemical potential. It provides a high energy density compared to its weight. Lithium-Ion batteries were first commercialized by Sony Corporation in 1991.

What is a Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) Battery?
The most obvious difference between Lithium Polymer batteries and Lithium-Ion batteries is the type of electrolyte used. A solid polymer electrolyte is used in the manufacture of Lithium Polymer batteries. This specific electrolyte acts as a plastic film that blocks electricity, while allowing for ion exchange. However, the Lithium Polymer batteries can offer better safety and can be manufactured in profiles with lower thickness. These characteristics make Lithium Polymer batteries ideal for thin and portable devices, such as mobile phones and tablets.
What are the Similarities between Lithium Ion and Lithium Polymer Batteries?
They Are Lithium-Based
Both types of batteries are lithium-based, which means that an electrochemical system is based on the movement of lithium ions.
They Offer the Possibility of Recharge
Both lithium ion batteries and lithium polymer batteries are rechargeable and can be used repeatedly many times.
They Provide High Energy Density
Both types of batteries have a high energy density per weight, which is ideal for light and compact devices.
What are the Differences between Lithium Ion and Lithium Polymer Batteries?
Their Electrolyte Structures Are Different
While liquid electrolyte is used in lithium-ion batteries, polymer electrolyte is used in solid or gel form in lithium polymer batteries.
Their Shapes and Formations Are Different
While the lithium-ion batteries are usually cylindrical or prismatic in structure, the lithium polymer batteries have a more flexible structure and can be manufactured in a wider variety of ways. Therefore, the lithium polymer batteries are preferred for thinner and lighter devices.
Their Security and Storage Conditions Are Different
The lithium polymer batteries usually have a better safety profile as the polymer electrolyte they contain carries less risk of explosion and they have a more flexible housing.
Their Costs Are Different
The lithium polymer batteries are usually more costly due to some aspects of their manufacturing process. This leads to the fact that lithium-ion batteries are generally used more widely.
As a result, although there are some basic similarities between lithium ion batteries and lithium polymer batteries, they are preferred in different applications due to their different electrolyte structures and housing structures.
How to Charge Lithium Ion and Lithium Polymer Batteries
Pre-Charging
The pre-charging stage takes place when the initial voltage of lithium batteries drops below 2.8V. As a general rule, the lithium battery voltage should not drop below 3.2V. Otherwise, the battery is considered dead and may need to be replaced. The batteries that have not been used for a long time may cause their voltage to drop below 3.2V. In this case, the device cannot be turned on normally or the batteries cannot be charged.
The pre-charging stage is important, as the battery can be damaged and its service life can be shortened if high current is applied to the dead battery when the charging process began. Therefore, the charging process of an empty battery should start with a current equal to 10% to 20% of the rated capacity of the battery. All professional chargers apply a pre-charging stage. In this way, you can ensure that your battery is restored.
Constant Current
If the voltage of the battery is above 2.8V or has reached this level during the pre-charging phase, the battery can be charged with a constant current, usually around 0.5C to 1C.
The charging speed of the battery is usually indicated on the data sheet and is typically between 0.5C and 1C. Some battery manufacturers may allow higher currents for faster charging, but if you are unsure or do not have access to this data sheet, it is usually safe to charge the battery at 0.5C. For example, if your battery is rated at 2,200 mA, it would be appropriate to limit the charging current to 1,100 mA. This way, you can charge your battery safely and effectively.
Constant Voltage
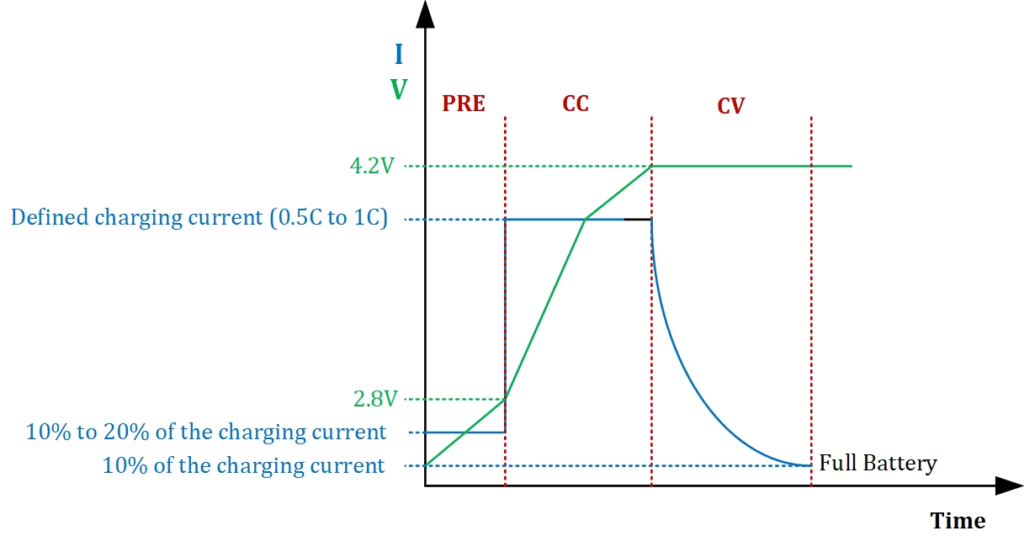
As can be seen in the table, after the battery reaches 4.20V, the current drawn decreases, and the voltage and current curves enter the Constant Voltage (CV) phase. 4.20V is a critical value and must be prepared with an accuracy of at least 1% or better, otherwise the battery may be damaged or explode.
The voltage is constant, but the current flow decreases until it reaches 10% of the charging current. For example, if you start the charging process with a current of 1100mA (0.5C of the 2200mA battery), you should stop charging at the 110mA threshold (which indicates that the battery is full). Many low-quality cheap battery chargers skip this CV stage and cut off the current when the battery voltage reaches 4.2V; however, a good charger should monitor the CV stage.



