Aluminum capacitors are passive components commonly used in electronic circuits. Its main function is to store electrical energy and then release when required. They further perform many different functions such as filtering, by-pass, coupling, timing and energy storage. The internal structure of the aluminum capacitor basically consists of a dielectric material placed between two aluminum foils.
What are different Types of Aluminum Capacitors?
- Aluminum Capacitors with Liquid Electrolyte: They include a liquid electrolyte. Such capacitors generally have higher capacitance values and are low cost.
- Aluminum Capacitors with Solid Polymer Electrolyte: They use a solid electrolyte. They stands out with advantages such as low ESR, high reliability and wide temperature range. They are particularly preferred for applications requiring high frequency and high performance.
- Hybrid Aluminum Capacitors: It is a specific type of capacitor that combines the advantages of aluminum electrolytic capacitors with solid polymer capacitors. These capacitors use a combination of liquid electrolyte and solid polymer electrolyte for offering enhanced performance and durability.
What are the Working Principles of Aluminum Capacitors?
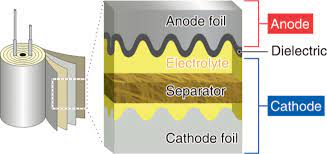
- Anode and Cathode: Aluminum foil is used as an anode electrode in aluminum capacitors, with its oxidized surface, thus forming a thin insulating (aluminum oxide) layer. This oxide layer is the dielectric material of the capacitor. A second aluminum foil called “cathode foil” is usually coated with an electrolyte.
- Electrolyte: The dielectric material in aluminum capacitors contacts with the liquid or solid electrolyte. This electrolyte constitutes the cathode of the capacitor and provides electrical conductivity.
- Polarization: Aluminum capacitors are polarized capacitors, meaning that they should be connected considering a specific direction. In case the anode (positive) and cathode (negative) poles are not taken into consideration, the capacitor may be damaged or may explode.

What are the Advantages and Disadvantages?

Advantages;
- High Capacitance Values: Aluminum capacitors can often provide high capacitance values in small sizes, increasing energy storage capacity.
- Lower Costs: It is a widely used economical solution as its production costs are relatively low.
- Wide Range of Use: It is widely used in a wide range of products such as power supplies, audio and video equipment, computers and automotive electronics.
- Wide Capacitance and Voltage Range: Aluminum capacitors offer a very wide capacitance and voltage range, making them suitable for many different applications.
- Energy Storage and Filtering: When used in power supplies, they are effective for filtering post-rectification fluctuations and storing energy.
Disadvantages;
- Polarization: Aluminum capacitors are polarized components, meaning that they should be connected considering a specific direction. Improper connection may damage or may cause the explosion of the capacitor.
- Limited Useful Life: Aluminum capacitors that use liquid electrolyte will expire over time due to the evaporation or drying of the electrolyte. This negatively affects the performance of the capacitor.
- High ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance): Particularly capacitors with liquid electrolyte generally have high ESR values. This can cause performance loss in high-frequency applications and circuits requiring high current.
- Leakage Current: Aluminum capacitors, in particular old and low-quality models, have a certain leakage current. This can cause loss of energy in the long run.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Their performance may vary depending on temperature. At high temperatures, the electrolyte may evaporate faster, shortening the useful life of the capacitor.
Which Applications are They Used For?

Aluminum capacitors are used in many different electronic applications due to their diverse properties and high capacitance values. Areas where they are commonly used:
Power Supplies
• Rectification and Filtering: They are used in power supplies to rectify and filter the AC signal to DC. They provide a smooth DC voltage by reducing ripples from rectifiers.
• Bypass and Decoupling: They are used to balance sudden voltage fluctuations in power lines and prevent undesired interference (noise).
Audio and Video Equipments
• Coupling and Decoupling: Capacitors are used to block the DC component and transmit only the AC signal when transferring audio and video signals from one circuit to another.
• Filtering: They are used to filter out undesired frequency components in audio and video signals.
Industrial Electronics
• Engine Drivers: They are used in engine drivers’ circuits to store energy and buffer against sudden load changes.
• Control Circuits: They undertake voltage regulation and filtering tasks in PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and other industrial control systems.
Computers and Telecommunication Equipments
• Mainboards and Graphics Cards: They are used in power distribution networks, in particular around high-performance components such as CPUs and GPUs, to store energy and reduce fluctuations.
• Telecommunication Devices: They are used for regulating the power and filtering the signal in modems, routers and other telecommunications equipments.
Energy Storage and Distribution Systems
• Renewable Energy Systems: They are used to store energy and compensate for sudden load changes in renewable energy systems such as solar panels and wind turbines.
• UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) Systems: They assume a critical role in energy storage and regulation in uninterruptible power supplies.
Consumer Electronics
• Mobile Devices: They are used for purposes such as storing energy and regulating power in mobile devices such as mobile phones, tablets and laptops.
• Household Appliances: They are used for power regulation and signal processing tasks in televisions, radio receivers, refrigerators and other household appliances.
Aluminum capacitors are preferred in a wide range of applications due to their high capacitance values and low costs. However, it is important to use and place them correctly due to their polarized nature and sensitivity to certain environmental conditions.





