Power conversion products are critical components to meet the different power requirements of electronic devices and improve efficiency. In this article, you can find basic information about these products.
1. LED Driver
What is a LED Driver?
LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a semiconductor, diode-based component that produces light when an electric current is supplied. They were invented in Russia in the 1920s and became a component that can be practically applied in America in 1962.
LEDs are more energy efficient than traditional light sources, have a longer service life and produce less heat. However, LEDs cannot work directly with the current or voltage received from average household or industrial electrical sources. Therefore, the LEDs need an LED driver to work correctly.
A LED driver provides the LEDs with the suitable current and voltage, ensuring their proper operation. These drivers convert the high-voltage current from traditional AC (Alternating Current) power sources into low-voltage DC (Direct Current) current needed by LEDs. In addition, the LED drivers protect the LEDs against overvoltage or overcurrent and provide a stable light output.
What are the factors that should be taken into account when choosing a LED Driver?
Type of Application: First, you need to determine whether the application requires constant voltage or constant current. LED lighting products usually need constant current, so a constant current source should be preferred if the source directly supplies power to the LED.
Output Power Compatibility: The output voltage or current of the LED driver must match the requirements of the fixture to be used. Insufficient power may prevent the LEDs from working correctly or affect their performance.
Protection Features: The LED driver should have protection circuits that can overcome the situations such as over-current, over-voltage and short circuit. This ensures the safety of both the LEDs and the driver.
Efficiency: An efficient LED driver saves energy and improves system efficiency. High efficiency means less heat generation and a longer LED life.
Power Factor and Harmonics: The power factor determines the energy efficiency and ensures the efficient operation of the electrical system. In addition, the harmonic levels should also be taken into account, as the low harmonic levels can damage the electrical system.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): It is important that the LED driver complies with electromagnetic compatibility standards. This allows it to work in harmony with other electronic devices and minimizes electromagnetic interference.
What are the areas of use of LED Drivers?
Home Lighting: LED drivers are widely used in indoor and outdoor lighting applications in houses. LED drivers can be found in lamp fixtures, spotlights, strip LEDs and other home lighting systems.
Street Lighting: LEDs are also frequently preferred in street lighting systems with their energy efficiency and long service life. LED drivers manage the power supply of street lamps and provide stable lighting.
Billboard and Signboard Illumination: Large billboards and signboards are usually illuminated with LEDs. LED drivers control and manage the light output in such applications.
Industrial Lighting: Factories, warehouses and other industrial facilities are usually illuminated with LEDs. LED drivers provide power management of industrial lighting systems and ensure long-term and reliable performance.
Automotive Lighting: In the automotive sector, LEDs are used in many applications such as headlights, taillights, signal lamps and interior lighting. LED drivers meet the power requirements of vehicle lighting systems.
Garden and Landscape Lighting: LEDs are widely used to illuminate garden paths, landscaping areas and other outdoor spaces. LED drivers also play an major role in these applications.
These are just a few examples of the common areas of uses of LED drivers. In short, LED drivers may be needed for LEDs to function properly in any kind of lighting or electronic system.
2. AC-DC Converters
First, let’s discuss the concepts of AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current).
What is AC?
It is the abbreviation of “Alternating Current”. AC is an electric current with a magnitude and polarity (direction) that changes repeatedly in time. Frequency is the number of times the current polarity changes in a second, measured in Hz.
What is DC?
It is the abbreviation of “Direct Current”. The polarity (direction) of a DC current does not change in time. A DC current is defined as the polarity (direction) and magnitude of the current do not change in time.

Although the polarity of the current does not change over time, the current whose amplitude changes is also defined as “DC” and is known as “Ripple Current”.

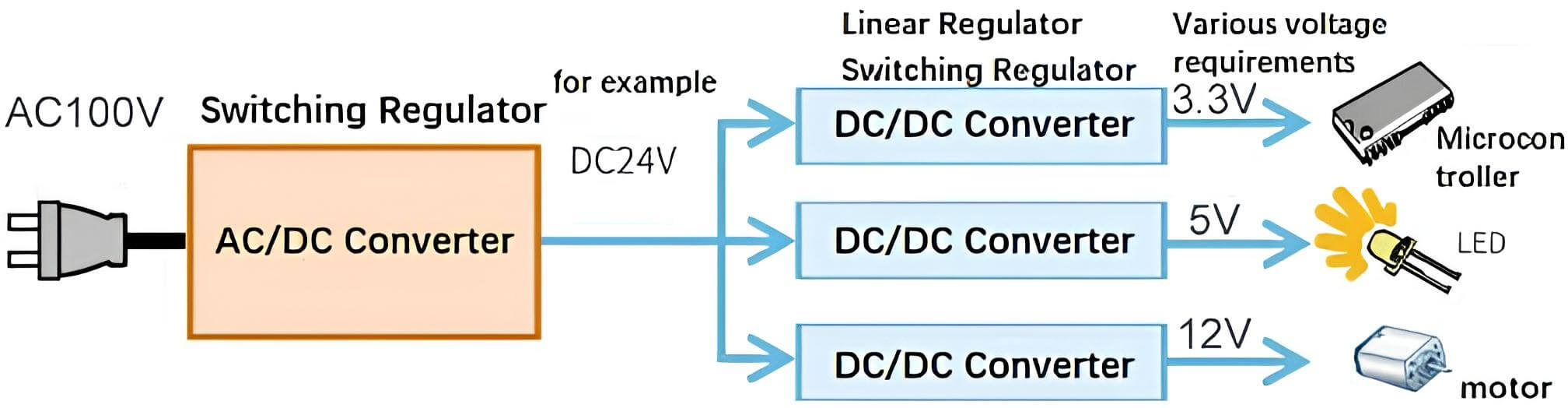
What is an AC/DC converter?
An AC/DC converter is a circuit element that converts AC voltage into DC voltage.
Why do we need an AC/DC converter?
Because the houses and buildings usually receive an AC voltage of 100V or 200V. However, most electrical equipment operates at 5V or 3.3V DC voltage. So, the AC voltage needs to be converted to DC voltage for the device to work. There are also some products that can work with AC voltage, such as motors and light bulbs, but since the motors are connected to the control circuit of the micro-controller and the light bulbs have already replaced with energy-saving LEDs, AC/DC conversion is still necessary.
Why is AC voltage used for transmission purposes?
At first, you can think as, ‘If a device is using DC, why don’t we send DC at the starting stage?’ – Hydroelectric power plants, thermal power plants, nuclear power plants and other sources of electricity are usually located in mountainous or coastal areas, and it is more advantageous to use AC voltage between these places and urban centers. In short, transmission loss (energy loss) can be reduced by transmitting AC power with high voltage and low current. However, since the high voltage cannot be used directly in a residential building, it must be reduced in steps via several sub-stations to be converted to 100V or 200V. Since AC is used in these conversions, the AC voltage is transmitted.
What does full wave and half wave rectifying (AC/DC conversion) mean?
When converting AC voltage to DC, there are two methods: full-wave rectifying and half-wave rectifying. In both cases, the forward current flow characteristic of the diode is used for rectifying. Full-wave rectifying is to convert the negative voltage component of the input voltage into a positive voltage, and then rectify it to DC voltage using a diode bridge circuit structure (pulse voltage). In half-wave rectifying, on the other hand, a diode is used to eliminate the negative voltage component at the input and rectify it to a DC voltage. Then, by the charging and discharging process of the capacitor, the waveform is rectified and converted into a pure DC voltage. As a result, full-wave rectifying, which does not use input-negative voltage components, is a more efficient rectifying approach than half-wave rectifying.
Under the same capacity and load conditions, the ripple voltage of full-wave rectifying is lower than that of half-wave rectifying. Higher stability and better performance cause the ripple voltage to be lower.

What are the areas of uses of AC-DC converters?
AC-DC converters has a wide range of areas of uses. Below are some areas where these devices are used:
• Computers and Mobile Phones
• Power Adapters (Wall Type, Desktop Type, etc.)
• Factories and Production Lines
• Power Supplies
• Solar Panels and Wind Turbines
• Substations
• Electric Vehicles
• Aircraft and Ships
• MRI Devices and X-ray Machines
• Hospital Equipment
• Battery Storage Systems
These are just a few examples for areas of use of AC-DC converters. These devices play a critical role in many parts of our modern life and are indispensable for energy conversion.
3. DC-DC Converters
What is DC?
It is the abbreviation of “Direct Current”. The polarity (direction) of a DC current does not change in time. A DC current is defined as the polarity (direction) and magnitude of the current do not change in time.

What is a DC/DC converter?
DC-DC converters are the electronic circuits used to reduce or increase the input voltage or current. For instance, if a device is powered by a 9V battery, this type of circuit can convert the input voltage to 6V or 12V. DC-DC converters are widely used in electronics, as different sub-circuits often need different voltages. In theory, we can provide each of them with a separate power supply, but converting the voltage from a single source is a simpler and more economical solution.

DC-DC converters can be found in almost any electronic device, but they are especially useful for portable devices, as they provide maximum power usage efficiency.
What does the concept of Linear and Switched DC-DC converter mean?
In linear converters, the voltage is reduced by a resistive load (usually a transistor) placed between the input and output. These circuits are simple and affordable, but they can only “reduce” the voltage. Also, if the input and output voltages are too different, they cannot offer high efficiency and may cause overheating.

In switched converters, power is applied in the form of pulse bursts regulated by a capacitor. These circuits can both reduce and increase the voltage, provide higher efficiency, but produce electromagnetic noise.

What does an isolated and non-isolated DC-DC converter mean?
In non-isolated converters, the input and output circuits are connected directly. In isolated converters, on the other hand, these circuits are separated by a transformer, which makes them safer for use in high-power devices.

What does Buck DC-DC Converter mean?
In Buck converters, the output voltage is lower than the input voltage. In these circuits, a conducting coil and a capacitor accumulate energy. When the voltage reaches a certain level, the switch turns off and the diode turns on. The self-induced EMF allows current to flow through the diode. The energy accumulated in the coil charges the load.

Such converters are used in battery chargers, multimedia players, game consoles, monitors and televisions.
What does the concept of Boost DC-DC converter mean?
Boost converters use the same components, but their layouts are different. The coil accumulates more magnetic field energy than in a Buck converter. When the diode activates, the input voltage is added to the energy stored in the coil, which increases the output voltage. Boost converters are widely used in hybrid vehicles, lighting systems using energy-saving lamps, portable lighting devices etc.
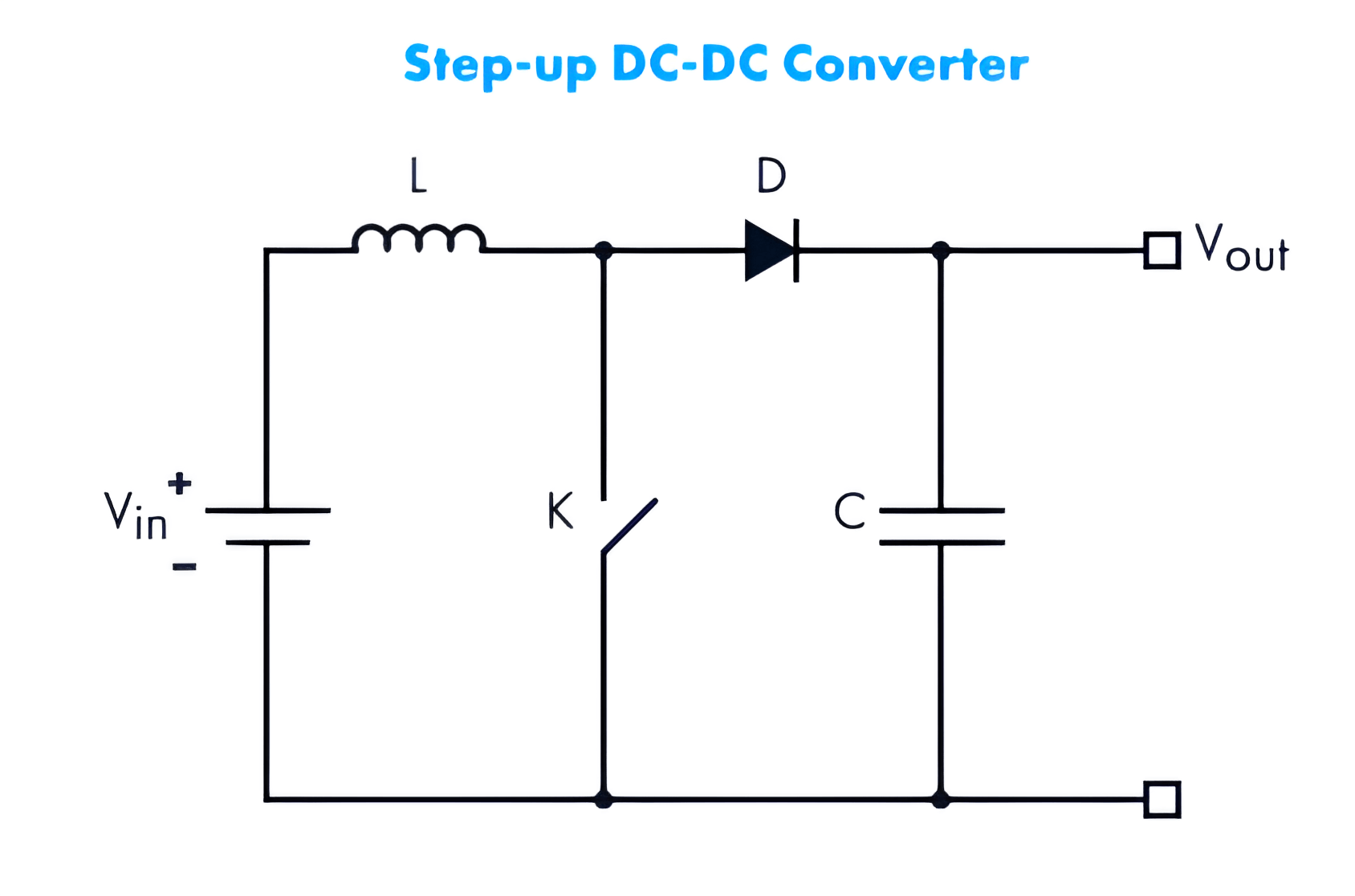
What is a Buck-Boost DC-DC converter?
These converters, also called ”Universal” converters, can both reduce and increase the input voltage and produce a higher or lower output level. These converters are particularly used when a wide input voltage range is encountered and it is necessary to bring it to a stable level. These converters are widely used in measuring equipment, photo and video cameras, MP3 players, GPS systems, wireless devices (keyboards, mouses, transmitters), LED lighting, etc.

What is an Inverting DC-DC converter?
These converters function like the Boost and Buck converters (can both reduce and increase the voltages), but they can also reverse the polarity of the output voltage. Such modules are used in cases where the device needs two sources.

What are the characteristic features of DC-DC converters?
DC-DC converter data sheets include the main parameters that describe the main characteristics of these converters. The following are some important characteristics that should be taken into account in the design phase.
Efficiency
Efficiency is the ratio of the input power reaching the load side. The efficiency of some DC-DC converters is over 90%. When using a DC-DC converter, it is necessary to make sure that the source supplying the power can provide sufficient power to compensate for the possible inefficiency of the converter.
Current rating
This is the maximum amount of current that a consumer should supply to a load of the DC-DC converter. The DC-DC converter can supply more current than this, but it heats up and may fail.
Temperature rating
This is the maximum ambient temperature at which the DC-DC converter must operate under full load. If this safety limit is exceeded, the DC-DC converter may overheat and be damaged, or turned off for protection purposes.
Ripple voltage
This rating measures the amount of ripple voltage at the output. Make sure that the ripple voltage capacity (rating) of the Buck converter meets your needs.
Regulation
This success criterion is related to how securely the output is controlled on the input voltage and load current. If a DC-DC converter’s regulation rating is 1%, the output voltage will not deviate from the nominal value by more than 1% within the specified input voltage range and output current range.
Voltage rating
DC-DC converters have some limits on how much they can convert a voltage (upwards or downwards).
Size and weight
DC-DC converters can be manufactured in small sizes, as they can operate at a very high frequency. Since some of the loss mechanisms increase with frequency, it causes them to be less efficient, so there is a kind of “exchange” between size and efficiency.
What are the areas of uses of DC-DC converters?
Mobile Devices: They are used to manage the battery voltage in devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets and other mobile electronic devices.
Power Supply: They are used as a power source for industrial equipment, computers, communication equipment and other electronic devices.
Automotive Applications: They are used for power conversion in in-car entertainment systems, navigation systems and other automotive electronics.
Solar Energy and Wind Energy: They are used to store and direct the electrical energy of renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines.
Telecommunications: They are used as a power source in devices such as telecommunications equipment and base stations.
Medical Devices: They are used for power conversion in sensitive electronic devices such as medical devices and equipment.




